Career and Technical Education (CTE) | Agricultural Science
What Are AFNR Standards?
Coming from a family of educators, Brad knows both the joys and challenges of teaching well. Through his own teaching background, he’s experienced both firsthand. As a writer for iCEV, Brad’s goal is to help teachers empower their students by listening to educators’ concerns and creating content that answers their most pressing questions about career and technical education.
If you teach in a CTE agricultural education program, chances are that you've heard about meeting AFNR standards. But what are these standards? Who sets them, and why is it critical to satisfy these standards in your classroom instruction?
In this article, you'll discover more about AFNR standards. Specifically, we'll look at:
- An Overview of the National AFNR Content Standards
- What Are the AFNR Foundational Content Standards?
- What Are Career Pathway Content Standards?
- How Can I Satisfy AFNR Standards in the Classroom?
After reading, you should better understand what AFNR standards entail so you can meet them in your agricultural education program.
An Overview of the National AFNR Content Standards
The Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources (AFNR) Career Cluster Content Standards were created by the National Council for Agricultural Education.
The Council was formed in 1983 to create agricultural education opportunities and support organizations, teachers, and students. The Council includes representatives from major agricultural education organizations and initiatives, including The National FFA Organization. They set priorities for agricultural education, including revising and updating CTE standards within the AFNR career cluster.
While you may already be meeting CTE standards in your classroom, such as the Common Career and Technical Core (CCTC) standards, each CTE pathway has specific instructional criteria.
The National AFNR Content Standards aim to create a coherent, universal set of educational criteria to help ensure CTE students in the Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources Career Cluster are prepared for future career opportunities. The content standards are a rigorous set of requirements designed to create an educated and competitive workforce in the agricultural sector.
When you follow the AFNR Content Standards, you ensure your students have the information, skills, and experience they'll need for occupations throughout the career cluster.
What Are the AFNR Foundational Content Standards?
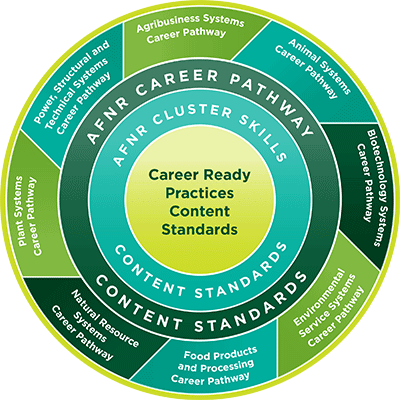
The AFNR Foundational Content Standards are an overarching set of criteria all students in agricultural science should master to be successful within the career cluster.
There are two levels of foundational standards: Career Ready Practices and AFNR Cluster Skills. Below, we'll examine both sets of criteria so you'll know how to include them in your instruction.
Career Ready Practices
Career Ready Practices consist of basic, universal skills students should master before entering the workforce.
Of the AFNR standards, they are the most general because they apply more to a student becoming a competent member of society rather than referring to specific training in agricultural skills. Developing these 12 transferrable skills will help learners be ready for any line of work, including AFNR occupations.
The top-level Career Readiness Practices include:
- CRP.01. Act as a responsible and contributing citizen and employee.
- CRP.02. Apply appropriate academic and technical skills.
- CRP.03. Attend to personal health and financial well-being.
- CRP.04. Communicate clearly, effectively, and with reason.
- CRP.05. Consider the environmental, social, and economic impacts of decisions.
- CRP.06. Demonstrate creativity and innovation.
- CRP.07. Employ valid and reliable research strategies.
- CRP.08. Utilize critical thinking to make sense of problems and persevere in solving them.
- CRP.09. Model integrity, ethical leadership, and effective management.
- CRP.10. Plan education and career path aligned to personal goals.
- CRP.11. Use technology to enhance productivity.
- CRP.12. Work productively in teams while using cultural/global competence.
By learning rudimentary skills like communication, leadership, and financial management, students will be better prepared to face the multiple challenges they encounter as working adults.
AFNR Cluster Skills
The Council's second level of standards is the AFNR Cluster Skills.
Unlike the Career Readiness Practices, these skills are directly related to careers in agriculture, food, and natural resources. These standards measure fundamental knowledge necessary for work in AFNR professions and concern the overall role of these occupations in society.
The primary AFNR Cluster Skills include:
- CS.01. Analyze how issues, trends, technologies, and public policies impact systems in the Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources Career Cluster.
- CS.02. Evaluate the nature and scope of the Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources Career Cluster and the role of agriculture, food, and natural resources (AFNR) in society and the economy.
- CS.03. Examine and summarize the importance of health, safety, and environmental management systems in AFNR workplaces.
- CS.04. Demonstrate stewardship of natural resources AFNR activities.
- CS.05. Describe career opportunities and means to achieve those opportunities in each of the Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources career pathways.
- CS.06. Analyze the interaction among AFNR systems in the production, processing, and management of food, fiber, and fuel and the sustainable use of natural resources.
By introducing students to subjects such as conservation and environmental stewardship, along with technologies and processes involved with the production of food, the AFNR Cluster Skills ensure that students can work cross-functionally to contribute to overall goals in the agricultural sector.
What Are the AFNR Career Pathway Content Standards?
The AFNR Career Pathway Content Standards provide tailored instructional guidelines for students in different pathways within the Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources Career Cluster.
Because AFNR covers a wide range of work opportunities, it's important that students receive the specific information they'll need to succeed in the career of their choice.
The eight career pathways are:
- Agribusiness Systems
- Animal Systems
- Biotechnology Systems
- Environmental Service Systems
- Food Products and Processing Systems
- Natural Resource Systems
- Plant Systems
- Power, Structural, and Technical Systems
Below, you’ll find the most significant content standards within each of these pathways.
Agribusiness Systems
Students in the Agribusiness Systems pathway are preparing for careers in the management of agricultural businesses.
To prepare students for successful business management careers, teachers must follow these AFNR pathway standards:
- ABS.01. Apply management planning principles in AFNR businesses.
- ABS.02. Use record keeping to accomplish AFNR business objectives, manage budgets, and comply with laws and regulations.
- ABS.03. Manage cash budgets, credit budgets, and credit for an AFNR business using generally accepted accounting principles.
- ABS.04. Develop a business plan for an AFNR business.
- ABS.05. Use sales and marketing principles to accomplish AFNR business objectives.
By following these standards, students will be able to handle the financial and organizational aspects involved in working in agribusiness.
Animal Systems
The Animal Systems pathway gets students ready to work directly with animals, including teaching health, nutrition, management, and processing.
For Animal Systems, agricultural educators should meet these criteria:
- AS.01. Analyze historic and current trends impacting the animal systems industry.
- AS.02. Utilize best-practice protocols based upon animal behaviors for animal husbandry and welfare.
- AS.03. Design and provide proper animal nutrition to achieve desired outcomes for performance, development, reproduction, and/or economic production.
- AS.04. Apply principles of animal reproduction to achieve desired outcomes for performance, development, and/or economic production.
- AS.05. Evaluate environmental factors affecting animal performance and implement procedures for enhancing performance and animal health.
- AS.06. Classify, evaluate, and select animals based on anatomical and physiological characteristics.
- AS.07. Apply principles of effective animal health care.
- AS.08. Analyze environmental factors associated with animal production.
When taught these standards, learners will know how to care for animals and their environment correctly.
Biotechnology Systems
In the Biotechnology Systems pathway, students use data and science to address problems across the Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources sector.
Specifically, teachers should satisfy the following pathway standards:
- BS.01. Assess factors that have influenced the evolution of biotechnology in agriculture (e.g., historical events, societal trends, ethical and legal implications, etc.).
- BS.02. Demonstrate proficiency by safely applying appropriate laboratory skills to complete tasks in a biotechnology research and development environment (e.g., standard operating procedures, record keeping, aseptic technique, equipment maintenance, etc.).
- BS.03. Demonstrate the application of biotechnology to solve problems in Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources (AFNR) systems (e.g., bioengineering, food processing, waste management, horticulture, forestry, livestock, crops, etc.).
When studying according to these requirements, students will be better prepared to safely work with biotechnology to handle problems and future developments in AFNR.
Environmental Service Systems
In this pathway, learners discover the systems, instruments, and technology used to preserve the environment and limit the impact of human beings.
For Environmental Service Systems, instructors should meet these criteria:
- ESS.01. Use analytical procedures and instruments to manage environmental service systems.
- ESS.02. Evaluate the impact of public policies and regulations on environmental service system operations.
- ESS.03. Develop proposed solutions to environmental issues, problems, and applications using scientific principles of meteorology, soil science, hydrology, microbiology, chemistry, and ecology.
- ESS.04. Demonstrate the operation of environmental service systems (e.g., pollution control, water treatment, solid waste management, and energy conservation).
- ESS.05. Use tools, equipment, machinery, and technology common to tasks in environmental service systems.
By following these pathway standards, students will be ready to address issues in environmental science, including using procedures and equipment specific to work within the career cluster.
Food Products and Processing Systems
This career pathway concerns fields like food safety, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, mainly when applied to the selection, processing, sale, and consumption of food and animal products.
To prepare students, teachers should follow these standards:
- FPP.01. Develop and implement procedures to ensure safety, sanitation, and quality in food product and processing facilities.
- FPP.02. Apply principles of nutrition, biology, microbiology, chemistry, and human behavior to the development of food products.
- FPP.03. Select and process food products for storage, distribution, and consumption.
- FPP.04. Explain the scope of the food industry and the historical and current developments of food product and processing.
In satisfying these standards, students will be able to handle the multidisciplinary work involved in the safe preparation and distribution of food.
Natural Resource Systems
Students pursuing this pathway are interested in managing our natural resources, including soil, water, forests, air, and wildlife.
To ensure students can work in diverse natural resource fields, they should understand how to:
- NRS.01. Plan and conduct natural resource management activities that apply logical, reasoned, and scientifically based solutions to natural resource issues and goals.
- NRS.02. Analyze the interrelationships between natural resources and humans.
- NRS.03. Develop plans to ensure sustainable production and processing of natural resources.
- NRS.04. Demonstrate responsible management procedures and techniques to protect, maintain, enhance, and improve natural resources.
When taught according to these pathway standards, natural resource systems students will have the knowledge and reasoning skills required to address a wide range of natural resource issues.
Plant Systems
Students in the plant systems pathway are concerned with understanding and managing plant matter, especially crops for harvest.
To prepare students, instructors should follow these pathway standards:
- PS.01. Develop and implement a crop management plan for a given production goal that accounts for environmental factors.
- PS.02. Apply principles of classification, plant anatomy, and plant physiology to plant production and management.
- PS.03. Propagate, culture, and harvest plants and plant products based on current industry standards.
- PS.04. Apply principles of design in plant systems to enhance an environment (e.g., floral, forest landscape, and farm).
By learning the basics of plant systems, students will gain a working knowledge that will help them manage plant products in their future occupations.
Power, Structural, and Technical Systems
The Power, Structural, and Technical Systems pathway deals with the fuel, technology, and machinery associated with the agricultural sector.
For success in this pathway, students need to:
- PST.01. Apply physical science principles and engineering applications to solve problems and improve performance in AFNR power, structural, and technical systems.
- PST.02. Operate and maintain AFNR mechanical equipment and power systems.
- PST.03. Service and repair AFNR mechanical equipment and power systems.
- PST.04. Plan, build, and maintain AFNR structures.
- PST.05. Use control, monitoring, geospatial, and other technologies in AFNR power, structural, and technical systems.
When taught following these requirements, learners will have a strong knowledge of agricultural infrastructure, including knowing how to operate specialized equipment.
Meet AFNR Standards with a Comprehensive Curriculum
To ensure your students are best prepared for work in the agricultural sector, it's crucial to meet AFNR standards in your classroom. In this article, you've learned more about how the National Council for Agricultural Education created these standards, why they're important, and how you can meet both foundational and pathway-specific criteria in your program.
However, to satisfy your AFNR standards while providing a quality learning experience to your students, you'll have to provide them with a relevant and engaging curriculum.
With iCEV, you can give your students a compelling learning experience that's continually updated to meet AFNR standards, so your students are ready for successful careers.